Operations, Customer Journey & Implementation
- Card Lifecycle Management
- How can I reload a payment account or card?
- Customer service and user claims in card issuing
- Tips to avoid problems when implementing card issuing
- How to prepare for a card issuing project?
- Payment schemes
- Card Benefits in card issuing projects
Card Lifecycle Management
Once launching card issuing projects, our customers usually forget that it is a long-term activity that requires constant verification and improvements. It is very important that you understand and manage your card holders and use best practices in card lifecycle management. Let me summarize key activities from a timeline perspective.
Stage 1 - choosing a card issuing partner
Obvious step. Everybody focuses on financials and technical integration. Very few people check value-added services and other products. Almost no one is aware of PCI DSS & other security requirements that will make your life easier on stage 4 and later ones. Another common mistake is that you do not check the financial stability of your card issuing partner as if it is not important for your business and users.
Stage 2 - implementation
Obviously important. No comments. Check Dev Zone and implement. Make sure your developers read specs carefully. Make sure you understand AML and KYC regulations so that you can comply with rules and the project can be built on strong fundamentals. A common mistake is not to consider Stage 4 - card lifecycle management processes are forgotten.
Stage 3 - launch
Everybody focuses on this moment, plans campaigns, distributes cards. And usually this is the last implementation step of this new product. It is a mistake.
Stage 4 - card lifecycle management
Once you are up and running, it is very important that you are able to monitor your portfolio, create reports, organise personalised campaigns and manage your portfolio in a very active way. There are several rules to follow in order to maximise your portfolio's earnings and performance. The most important ones are summarised below:
- Portfolio Manager - have people that will be responsible for the management of your portfolio. 1 person is enough at the beginning. Make sure these people understand goals and work to make your cardholders active
- Reporting system- make sure you have a flexible reporting system that gives you information not only about the number of issued cards and transactions, but more importantly on the behaviour of various customer groups:
- have reports how many customers used the card after 1-2 days, be able to find the user IDs
- have reports with customers that used the card after 5 days, 15 days, 30 days
- have reports on inactive customer groups
- Actions - be ready to act basing on the user behaviour
- once you see that your customer is not using the card after 1-2 days - send him/her a notification or an educational reminder
- once you see that the customer is not using the card for 15 days - maybe you should send a small digital gift to the customer and deliver it if he/she starts using card
- if you see an inactive customer after 30 days - ask them why they are not using the card; maybe you will get a correct feedback
- Reporting - again and again check if your actions work correctly. What is their success rate? How are your customers changing their behaviour?
- P&L analysis - make a detailed analysis from a financial perspective, incentivise users to do transactions that are bringing more revenue, think of increasing monthly fees for non-active users
- Quality reporting - check the quality of your services, ask users for feedback regularly, collect information, analyse it, make actions to improve
- Value-added services - think of launching new services that can improve performance of your portfolio. Maybe a voucher-based ending, card-to-card money transfers, loyalty programs etc. Ask us for best practices and tools that are easy to use.
- Education (super important) - never underestimate the importance of educational messages. You can teach customers how to use the card on the internet, tell them how to tokenise the card in Apple or Google Pay, show them how to pay at ATMs. Card issuers tend to forget how cheap and profitable it is to work on user education. Do not assume that everyone everywhere uses payment cards the way you use them today. People sometimes do not know how to use 3DS, they are afraid to use it, etc. Work on that.
- Learn, change, improve...
Card issuing is a long-term activity. Please do not think that you will launch it and everything will work properly. You should be constantly working to attract more users and teach existing users how to use the cards so that they add real value to your business. Good luck!
Thanks for reading.
How can I reload a payment account or card?
There are many ways of transferring money to payment accounts or cards. In this article we would like to explain how it can be done with Verestro and in other cases.
Let's start with definitions so that we speak the same language. What is a payment card? What is a payment account? What is an IBAN? It seems simple, but in fact many customers use these words in a different way.
- Payment Account - it is a place in the system of a payment institution which holds information about money stored for a particular customer. Just it - a kind of a Record ID in a payment institution. It is not an IBAN, it is not a card.
- IBAN - IBAN is a payment account number in an international banking standard. This number helps sending wire transfers to a Payment Account.
- Payment Card - it is another number (PAN - Primary Account Number in the terminology of Mastercard and VISA) connected with a Payment Account and usually another payment instrument connected with a Payment Account. The Payment Card is a tool to pay using money on a Payment Account and sometimes it is a way to transfer money to a Payment Account. To be honest, I do not know situations where a Payment Card works without a Payment Account. In some countries (like USA) usually a Payment Account is not used in common discussions, but in fact there is always a Payment Account connected to a Payment Card.
Once we know those 3 definitions, let's look at the ways of transferring money to a Payment Account, which in other words could mean ways of reloading a Payment Card. There are several ways that we can use:
- Bank transfer to IBAN - in such a case the user is sending money from an external bank account to our Payment Account, using an IBAN connected with our Payment Account. Usually it is a very easy, fast and effective way of transferring money in case of domestic transfers. It could be a costly way of reloading an account if the customer is abroad.
- Payout to Card - in such a case the user is sending money from another bank or money transfer organisation using a Payment Card number issued by Verestro and our issuing partner. The customer is using Mastercard Moneysend or VISA Direct to transfer money from another account to their Payment Account at Verestro. Usually it is very fast but not cheap way of money transfers.
- Card-to-card - card-to-card transfer is used when the user provides at external service another Mastercard or VISA card and transfers money to a card issued at Verestro. In such a case a funding card (a card issued by another bank) is debited and our Payment Card is credited, which means that money will appear on the Payment Account soon.
- Reload by another card via PSP, Google Pay or Apple Pay - in any wallet of our partners we can provide functionality called Paytool which enables charging another card and sending money directly to the user's Payment Account. In this situation a funding card is charged as if it was an eCommerce transaction. The user's Payment Account can be reloaded quickly.
- Reload by partner - in many cases our partners can use their own funds to reload the user's Payment Account. Examples of such situations are lending institutions that issue a card and reload a Payment Account with a loan amount. Similar example could be issuing cards for insurance related claims - in such a situation our partner (insurance company) adds money to the user's card and sends the card to the insured person. Usually such a reload happens via MasterBalance which is an account that we hold for our partners and it contains their money. This account can be used for a reload, as is usually used for transaction processing.
- Reload by crypto assets - in some cases it is possible that our partners send crypto assets and we will convert them in cooperation with our partners into FIAT currencies to reload the user's account.
- Openbanking - our partners can use open banking PIS (Payment Initiation) messages to transfer money to the user's Payment Account. We can help with such reload tools using our Paytool product.
Those are ways of reload we use today. We are happy to work on other ways of money transfers and enable new ones.
Thanks for reading.
Customer service and user claims in card issuing
Once you start issuing cards for your users, you will experience a wide range of various problems and requests coming from your customers. In this article we will summarize the most common issues, so that you can get prepared.
These include:
- Transactions not working
- Problems with delivery or activation of plastic cards
- Transaction reversals and refund issues
- Fraudster activity
Point 1 - Transactions not working
The most common problem after starting card issuing is connected with performance of transactions. Your users will inform you about problems with transaction authorisations or merchants not accepting their card etc. There can be plenty of reasons for such problems. The most important are:
Point 2 - Problems with delivery or activation of plastic cards
Usually, when you decide to use not only virtual, but also plastic cards, you will experience various problems with personalization, delivery or activation of plastic. In different countries there may be various issues with these processes. They are usually connected with logistics or lack of easy activation methods for cards. Some of those issues can be cleaned by us during the project, but for many of them we will not have a good solution. Actually, in today's digital world, we do not recommend issuing plastic cards, but if you need to do so, get ready for such problems.
Point 3- Transaction reversals and refund issues
White paying with cards, customers will experience situations that they want to resign from a transaction after some time. Sometimes immediately - and in this case reversals will be used. Sometimes after several days - in this case refund will be used. In such situations we should receive an authorization from the merchant or acquirer that credits the transaction. We should be able to deliver this message to you, so that you can increase the user's balance on account. But sometimes this process does not work correctly. If the card issuer does not receive a message from the acquirer or payment scheme, we are unable to give you this information. User's funds may get frozen for 2-4 weeks. It is important that you understand that such things happen.
Point 4 - Fraudster activity
Any new payment activity in the world is attracting the attention of fraudsters or payment mafias. There are people in the world specialised in stealing card data or making transactions with cards while having no money on accounts. This is a very serious risk for you, as they will be testing your systems as well. This is especially visible if you have many "Do not honour" transactions or weak Know Your Customer processes. Be ready for it. Monitor your traffic. Cards will not always work for all payment transactions, some fraud rules will block suspicious activities, but your online monitoring is necessary.
Those are key points to remember about. Please do not forget about them while launching your card issuing program with us.
Thanks for reading.
Tips to avoid problems when implementing card issuing
So you have a good business case for issuing cards for your customers and you found a perfect vendor who can provide formal and technical services in this area. Right after signing the contract you’re ready to implement. What now?
Now it’s time to make sure that the implementation will be as smooth as possible and you and your team won’t get stuck on some of the common problems that may happen in the project. Of course each vendor has his own approach, but let us explain how to avoid some of them based on Verestro’s experience.
Preparing everything for you takes a moment
Depending on your particular setup we will need 4-8 weeks to prepare everything for you. From dedicated environments so that your customers and their cards will always be safe and secure, to ensuring that you will be able to use the cards in Apple and Google wallets and that your proper logo will appear in the 3DS confirmation screen when customers will be paying online. In the meantime you can focus on understanding all the APIs using Sandbox environment and make sure that your team is ready for the work in front of them – for example by analyzing the documentation carefully. Our services will be available for you one by one, so you don’t need to wait full 8 weeks to start implementation – usually first work on your side starts after 2-3 weeks from the kickoff meeting.
Test and adapt
Everyone is always eager to launch the product to final customers – that’s obvious. But it’s good to plan an extensive testing phase that will limit the potential volume of incidents that may happen once you’re live. A simple successful transaction done in ecommerce and brick and mortar POS is a very good prognosis, but should not be the end of testing phase. Take into account different scenarios and edge cases (like reversals and refunds – or even partial reversals). Take into account that there are many players in the world of payments and that a simple transaction is actually a connection of several backend systems (acquirer, issuer, payment network, additional vendors). The more you test, the less surprises will be there in the end.
Knowledge and understanding is key
Issuing cards and processing transactions is unfortunately not like riding a bike – it’s easy to forget. During the project with Verestro you’ll learn a lot about the world of payments and cards. Make sure this knowledge is gathered on your side and distributed between team members.
Plan your MVP
Rome wasn’t built in a day. Best banks did not simply appear in a moment. Issuing cards is a vast topic that requires a lot of iterations to make sure the basics are solid. It’s always good to start with essentials:
- Create user
- Create their balance
- Issue first card
- Digitize the card in Apple/Google Wallet
- Make first eCommerce transaction (with 3DS)
- Make first POS transaction
- Run ‘friends&family’ phase within your company
- Then start adding features and more functionalities
If you’ll start focusing on ‘nice-to-have’ features too early in the process, you may loose sight of more basic processes what may cause delays in the whole project.
Having all of that in mind should make your project more streamlined and effective.
How to prepare for a card issuing project?
Do you want to issue cards to your users? In this article we describe what is required on your side to implement virtual or plastic cards in your applications.
Let's imagine you are a fintech, crypto wallet, lendtech or any other company with a concrete target segment, some or thousands of users and you have a mobile application for your customers. You have decided to go live with card issuance in order to increase revenue and user loyalty. Below we describe the main decisions and steps you need to take to get ready for a card issuing program:
- Decide on a card issuing partner - check out other articles we have on this topic in the Knowledge Center. Make sure that the partner has the necessary functionalities, legal requirements and flexibility that you can accept. Check your partner's financial standing. Contact us for more details.
- Analyse and describe your use cases - describe user flows, develop some initial graphs of how key processes will work. Focus on user onboarding, Know Your Customer steps, card generation and activation, card management and transaction flows. Read the Developer Zone requirements during this step to make sure you are ready to integrate without difficult customisations.
- Check the legal environment - try to analyse and understand the regulatory environment. Check if you can fulfill KYC requirements and how you can collect data from users. It is important that you submit a user selfie and document photos to the card issuer during the verification process. If you are working with us, please make sure that you have a European entity or branch in the EU to sign a contract with us for card issuing.
- Verify API integration - go to the Developer Zone and analyse APIs or SDKs that you will have to connect to. If you want to avoid PCI DSS audits and associated costs, consider using SDKs. It is highly recommended if you have a large group of users.
- Make P&L analysis - consider the revenues from card issuing and the costs of this product. Make sure you understand unit economics. You can use articles in our Knowledge Center to start this work. Choose an affordable partner - do not think that if something is more expensive, it is better in quality. The card issuing business is a cost-based business where low level unit economics matter, especially cost per card and cost per transaction. Revenue share from interchange fees or currency conversions is even more important than costs.
If you have checked these points, you are ready to sign a contract. Contact us sooner, let's work together. We can advise you on many of these points to build the best possible program for you. We have extensive experience in more than 30 countries on 5 continents. Make use of this knowledge to get started.
Thanks for reading.
Payment schemes
In this document we describe how payment schemes (Mastercard and VISA) work.
Payment card business is a large global market, which was developed in the USA in the first half of XX century and has grown globally. In this document we will describe the main business principles and in the next chapters we will go into more details. We will focus mainly on Mastercard and VISA operations, as these are the largest payment schemes in the world and the main partners we work with.
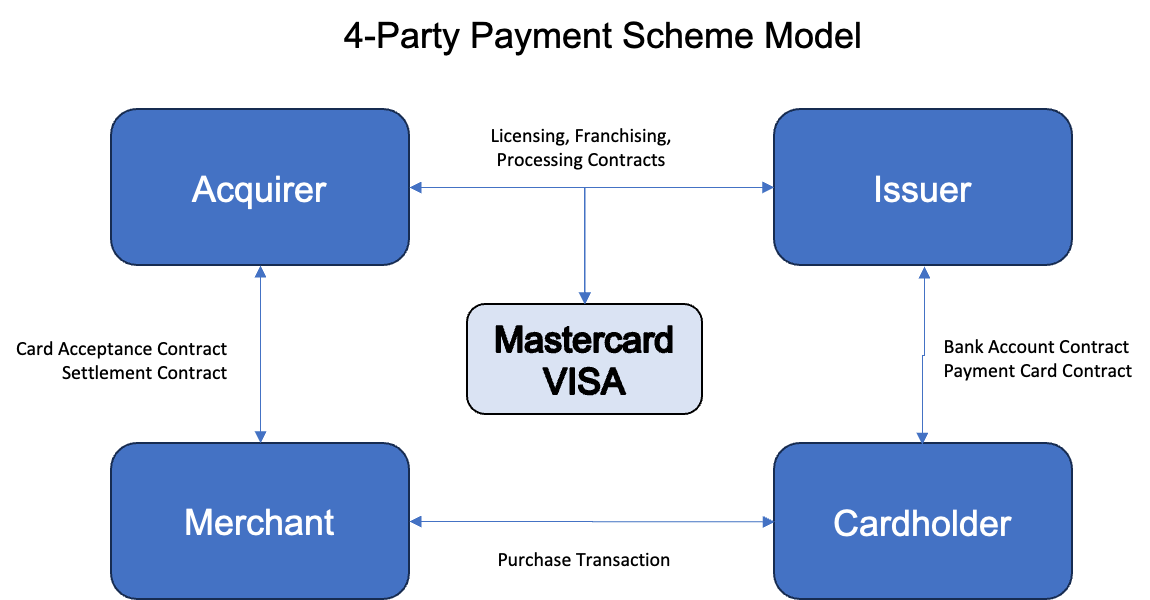
Four Party Model
Let's start with the general relationships between the parties. In the Mastercard and VISA 4-party model (which is actually 5-party model) there are the following players:
1. Cardholder - has a contract with Card Issuer, which is usually a bank, financial institution, payment institution, credit union, etc. Cardholder keeps a card in a plastic or virtual form that he/she gets from Issuer. Cardholder makes a purchase transaction at Merchant or sometimes withdraws money from an ATM. In the case of an ATM transaction, the ATM operator (usually a bank) acts as Merchant in a standard purchase transaction.
- Cardholder is happy because he/she does not need to carry cash all the time and has money all the time in their pocket or phone.
- Cardholder has to pay card fees to Issuer for getting a payment card.
2. Merchant - delivers goods to Cardholder, but does not receive cash immediately, but accepts the card transaction, which gives him/her almost 100% confidence that he/she will receive money in a few hours or days.
- Merchant is happy because he/she sold goods, usually having sold more than Cardholder could afford with cash. Imagine the situation where you have to pay cash all the time. Would you always carry enough cash with you? What if you want to buy something, but you do not have enough cash?
- Merchant has to pay the so called "Merchant Fees" to Acquirer for processing the transaction. Usually, Merchant Fees are between 0,5-3% depending on transaction value, country, merchant segment, type of card etc. Merchant fees cover most, if not all, of the transaction processing costs. They usually include all the fees charged by Acquirer, Issuer, Mastercard or VISA for the transaction.
3. Issuer - Issuer is usually a bank, credit union or any other payment institution that delivers payment cards to cardholders (consumers or businesses). Issuer signs contracts with cardholders. On the other side of business, Issuer has a franchising or licensing contract with VISA and Mastercard and connects to their network using Issuing Processors. Verestro and our partners (for example Quicko) plays the role of Issuer and Issuer Processor in our card issuing or BIN sponsorship projects. During the transaction process, Issuer usually gets authorization, clearing and settlement messages that result in transfer of money from a cardholder account to Acquirer so that Acquirer could settle the transaction with Merchant.
- Issuer is happy because they charge card fees to Cardholder (for example monthly per card) and get transaction fees called Interchange Fee from Acquirer. Interchange fee is a very important part of Merchant Fees. In the European Union for consumer cards it is usually in the value of 0,2-0,3%, but in many countries, especially for business and credit cards, it can amount to 1-2% of the transaction value.
- Issuer has to cover costs of card issuing, which include:
- Cost of payment scheme (Mastercard or VISA) incl. monthly connection, license, authorization, clearing and many many other fees. This is usually the main part of Issuer's costs.
- Cost of other processors incl. transaction authorisation, card maintenance, card tokenization, plastic card manufacturing, personalisation, delivery, etc.
- Regulatory costs incl. payment license operations, Anti-Money Laundering processes, etc.
- Various costs connected with maintaining a relationship with Cardholder incl. proper communications, SLAs, etc.
4. Acquirer - Acquirer is usually a bank or payment institution that signs contracts with merchants, settles payment transactions with merchants and has acquiring contracts with a payment scheme. Acquirer usually provides a payment terminal to merchant locations, and makes sure if it works and is ready for transactions.
- Acquirer is happy because they charge Merchant Fees that usually consist of transaction fees (0,5-3%), sometimes fixed fees per transaction (0,01-0,5 EUR) and monthly fees per terminal.
- Acquirer needs to cover various fees, including regulatory fees, payment scheme costs, cost of processors, terminal purchase and costs of operations.
5. Payment Scheme - Payment Scheme (i.e. Mastercard or VISA) are key for keeping the model running. They develop technical systems that issuers and acquirers are connected to, they process transactions, they develop the market. However, they are also the biggest beneficiaries of the market growth as every new transaction represents revenue for Mastercard and VISA.
Key Processes
There are several processes that take place during card and transaction processing, and here we will briefly describe the most important ones:
- Card issuing process - this process or set of processes consists of multiple actions that Card Issuer needs to perform to issue a payment card. They are the following:
- regulatory compliance - every card issuer in the world needs to comply with law, get license from a national bank or financial regulator, work according to their recommendations and rules,
- Mastercard integration and licensing - it consists of a formal process, providing necessary cash collaterals, doing technical integration, getting security certifications etc.,
- card creation process - after signing a contract by a user, Card Issuer needs to create a new card number (using BIN of the issuer - BIN = first 6 or 8 digits of card). When a card number (PAN = Primary Account Number) is created, the card can immediately work as a virtual card or can be sent for personalisation if it is a plastic card. Usually, after the user receives the card (virtual or plastic), the user starts the card activation process, sets the card PIN and can start using it.
- Transaction process - this process consists of several operations that result in transfer of money from Cardholder account to Merchant. They are the following:
- Authorization process is an action that ensures that Merchant can immediately get information if Cardholder has money on his/her card account and if this card is not stolen. The authorisation can happen online (a direct request to Issuer's system to check the balance and card status) or offline (in this case a chip on the card makes a decision if it can approve the transaction without asking Issuer's systems).
- Clearing process is an action of payment scheme during which clearing files are delivered by acquirers to payment scheme and payment scheme calculates how much money each Acquirer should receive from each Issuer in the world.
- Settlement process is a process of transferring money from issuers to acquirers and later to merchants so that finally Merchant receives the transaction amount, less Merchant Fees, on his/her bank account. Every Issuer and Acquirer has settlement bank accounts that are used for transferring money from or to. Payment Schemes operate those accounts using something like Direct Debit / Credit to transfer money between Settlement Accounts of various financial institutions.
- 3DS - sometimes additional authentication mechanisms are used to ensure that the person initiating the card transaction is the actual cardholder. In the case of eCommerce transactions this process is called 3DS. During an Internet transaction, the user's browser opens the bank's website, where the user can authenticate the transaction using one-time passwords or other forms of authentication developed by Issuer. After the 3DS authentication is verified, Acquirer receives a special cryptogram that is included in the authorization message and validated later by Issuer during the authorization process.
- Tokenization - tokenization is a process of exchanging a real card number into a token number (similar to a card number) to enable digital and contactless payments. Usually it is connected with transactions performed in cooperation with the so called X-Pays (i.e. Apple Pay, Google Pay, Fitbit Pay etc.). The process of tokenization requires an integration with Mastercard Digital Enablement System (MDES) or Visa Tokenization system (VTS) to enable tokenized payments.
- Refund and reversal - special type of transactions that enable reversing payment transaction either immediately (reversal) or later (refund). Once this process has been initiated, Cardholder can receive money back after successful authorisation.
- Chargeback - process of complaint management. It can be initiated by Issuer in case Cardholder informs Issuer that he/she did not do the transaction or did not authorize it, or goods were not delivered etc. The process is costly for Issuer and Acquirer but ensures security of the system for cardholders.
- Card-to-card transactions and payouts - the so called "payment" or "credit transactions". In a standard purchase transaction money is transferred from Cardholder to Merchant. In a card-to-card transaction or payout transactions, the user gets money on his/her card or on the account linked to the card.
There are other important processes associated with payment systems and card transaction processing, but let's stop here and take a short break to understand these critical processes.
Card Benefits in card issuing projects
Once you are launching your card program it is important to think about additional benefits that you can deliver for your users or products that can increase the value of your program. In this article we will show a few ideas and examples that you can use to enhance your card issuing project.
How to strenghten your card issuing program?
- Education and messaging - the most important but very often forgotten. No cost benefit. Just start teaching your users how to use cards, how to behave in a secure way, how to pay on the internet, how to connect to Apple Pay or Google Pay etc. Build ways or use our white label ways of communication. It will pay back for sure.
- Enable new ways of payments - enable new ways of payments for your users. Teach them how to use their card in a friendly, secure, internal environment. Maybe they can buy something on your platform, maybe you can enable money transfer from cards etc. Thanks to such activities you will teach them how the card works and what they can experience. You will lower the level of fear and risks they may fear at Point-of-Sale.
- Insurances - think of launching a program with insurances. This became very popular 10-20 years ago in the card business. Many banks give users additional insurances that they can buy in their apps. Insurance is an ideal product and card benefit because it increases security feeling among your users. Examples of such insurances are eCommerce payment extended insurance, lost & theft insurance, travel insurance etc.
- Point based loyalty program - think of launching a point based loyalty program or join an existing one. We are using the Priceless Specials program done by Mastercard. This can be a strong added value that you can communicate. You can also increase revenues thanks to it and increase cross-selling if you start giving points to users for using non-card based services that you are selling. It may seem difficult to implement but actually it is not.
- Voucher based loyalty program - once you have a growing number of users you can start arranging special promos with eCommerce or offline merchants. We can help with it as we are building a network of such partners. Thanks to such activities your users will get additional margin or cash back and it will increase retention and happiness of your customers.
- Premium cards - maybe it is worth thinking of launching new gold, platinum or World Elite cards for your users. Maybe you could offer much better VIP service, together with a concierge for much higher fees. It is very popular among banks and it is one of the easiest ways to increase profitability of the portfolio.
There may be more activities but these are the ones that you can implement relatively quickly in order to offer better service and increase revenue.